If you are on the enterprise plans of Office 365 (E4 for example), your users may be eligible to use Microsoft's enterprise social network called Yammer. This article will cover a few questions I was curious about when rolling out Yammer as well as what to expect.
How do I tell if I am eligible?
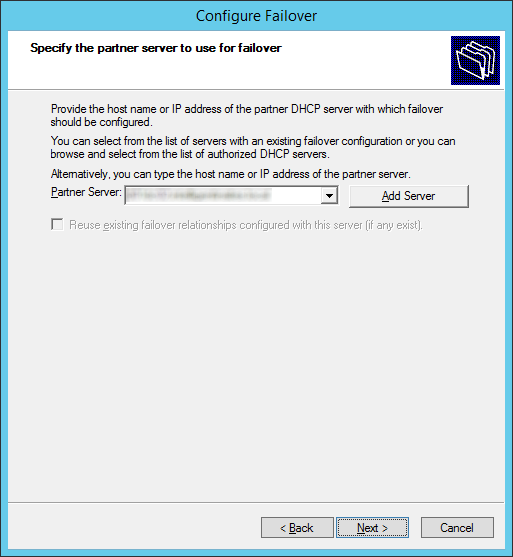
- Login to the Office 365 admin portal (https://portal.microsoftonline.com)
- Click on included services on the dashboard

How do I activate Yammer?
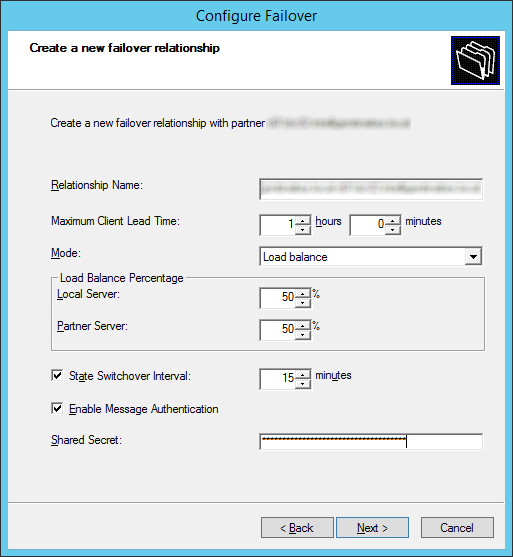
- If you are eligible for the Yammer service, click on the Yes, activate Yammer Enterprise for my network

- Click on the Activate Yammer Enterprise button
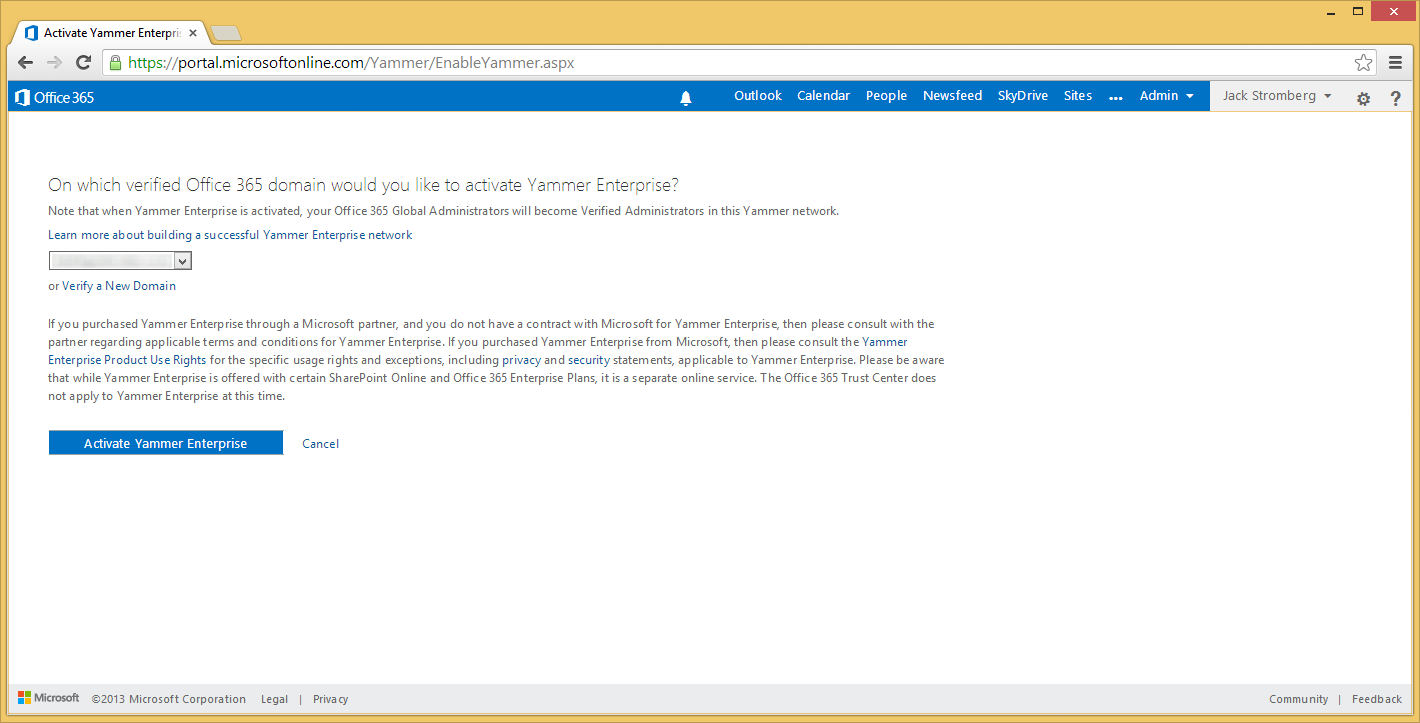
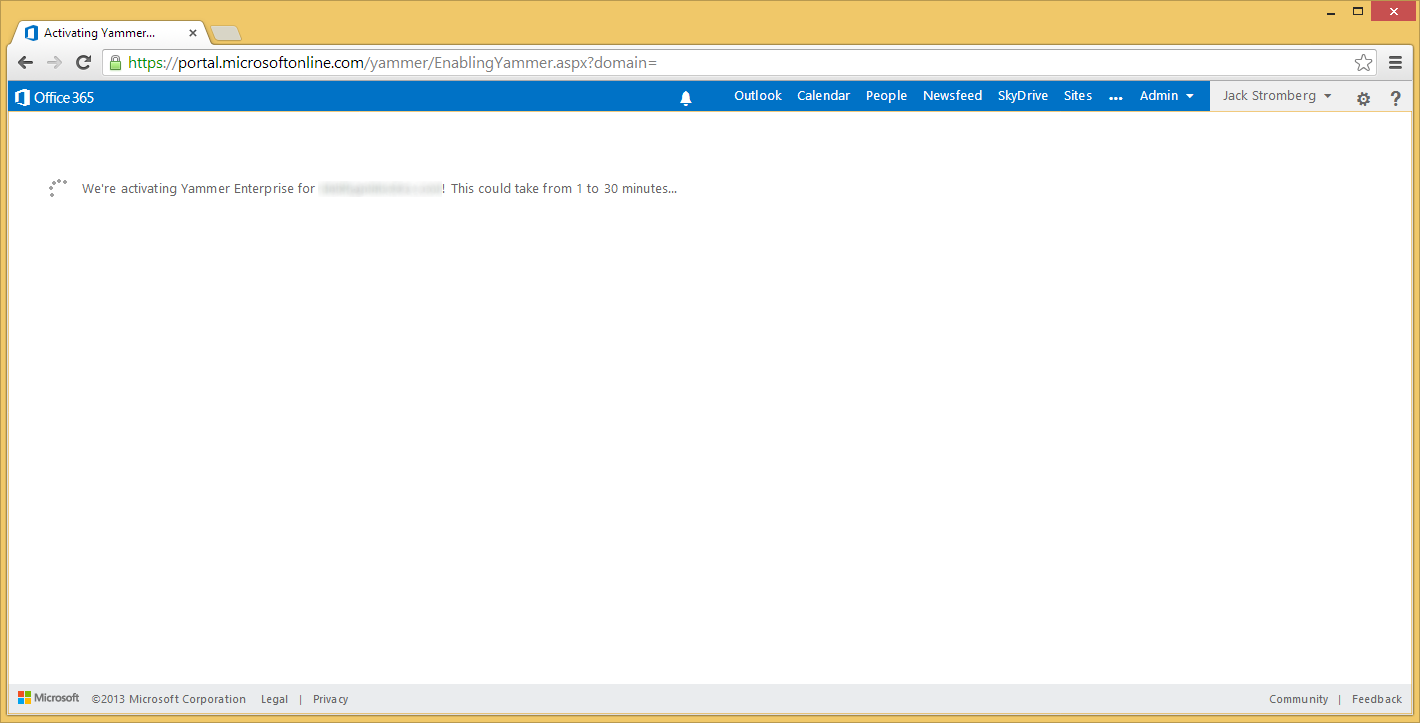
- You will be redirected to a screen where you see a loading bar. Grab a can of pop/coffee/tea/water and come back.
- Click on the Create Yammer Account link once Yammer Enterprise has been provisioned.

- Type in the same email address you use for your Office 365 Admin credentials
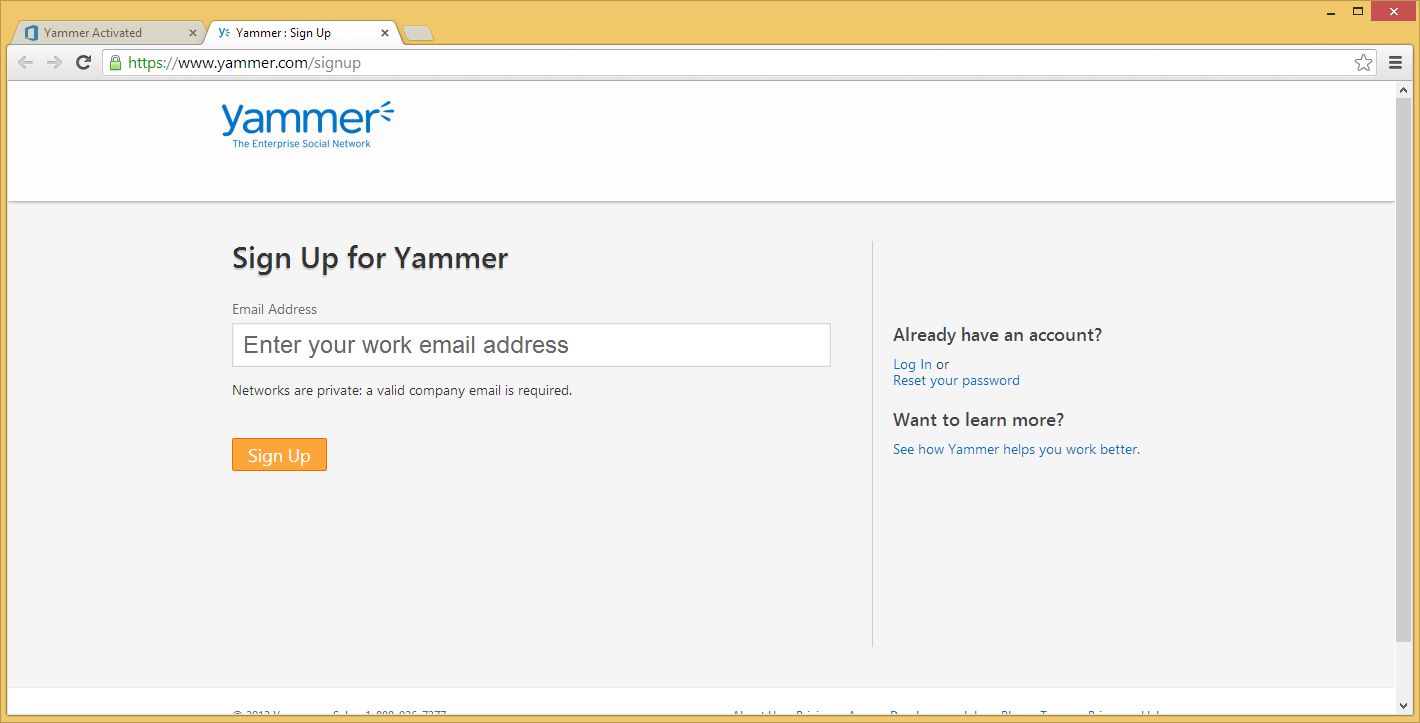
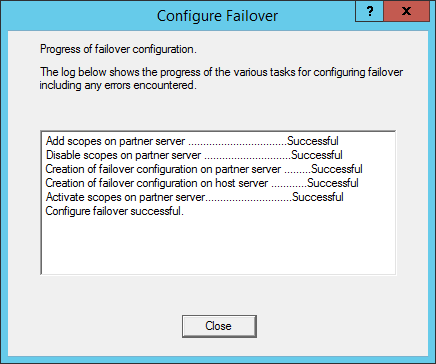
- If successful, you should see the screen below:
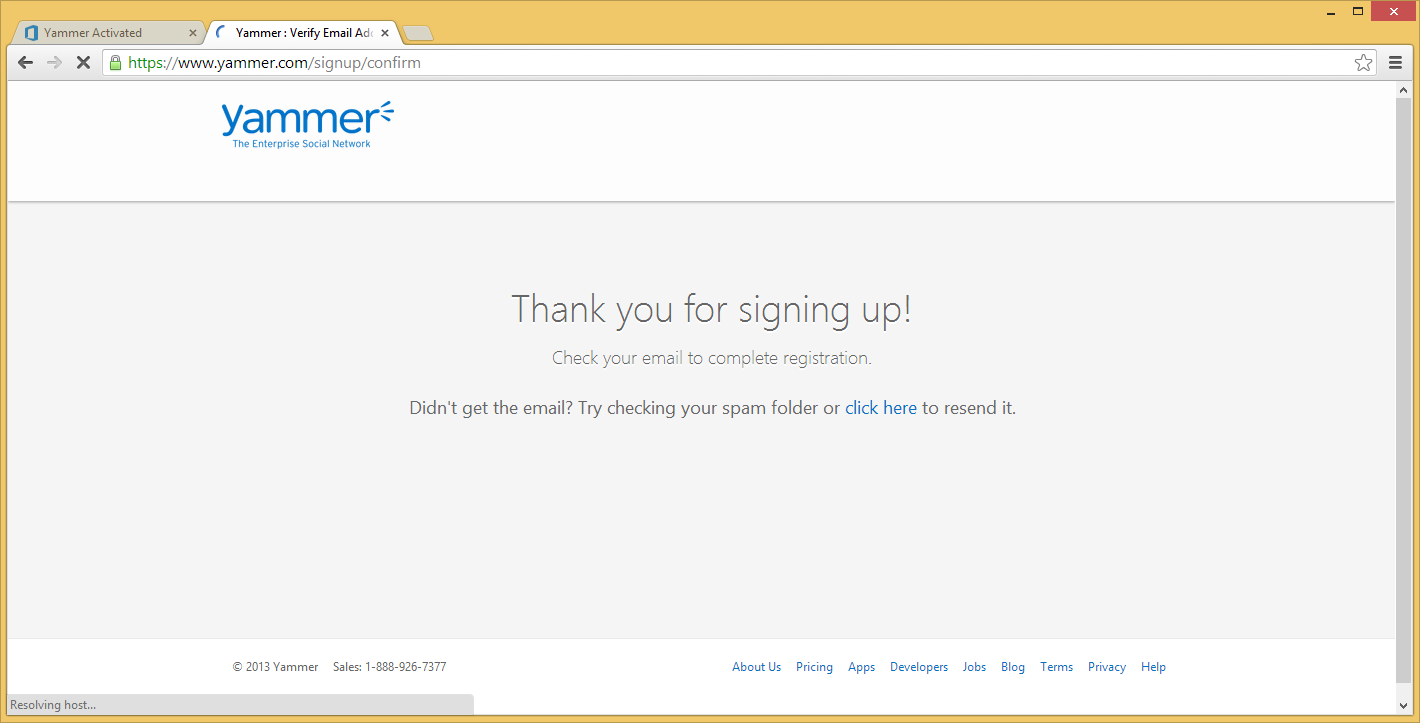
- Check your email and click on the Complete Signup button
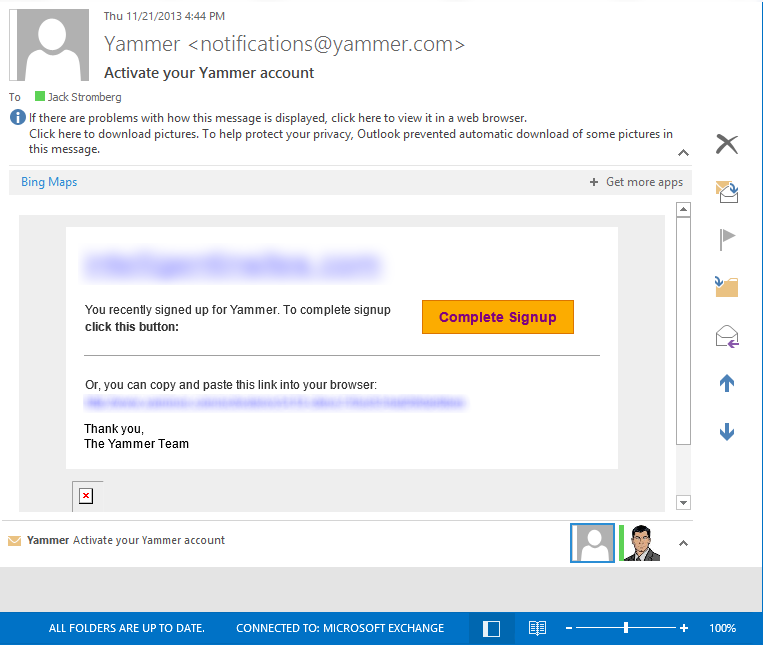
- Type in your information and click the Next button
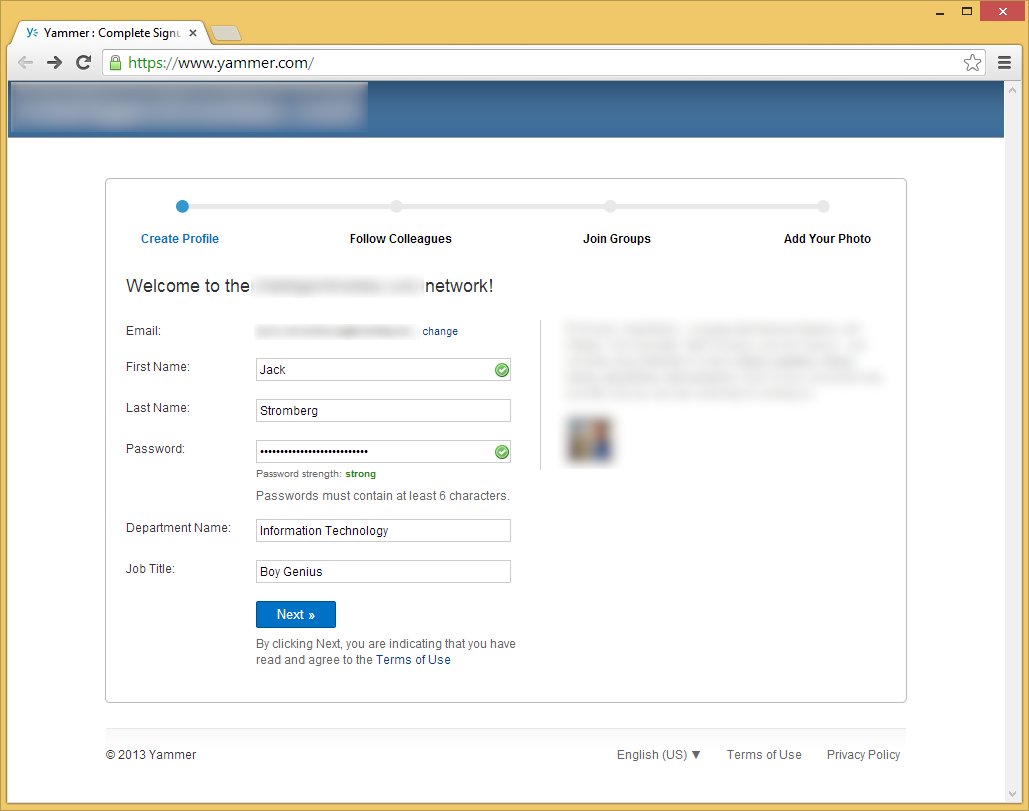
- Click Next on the who do you work with page, or spam your colleagues to sign up as well.
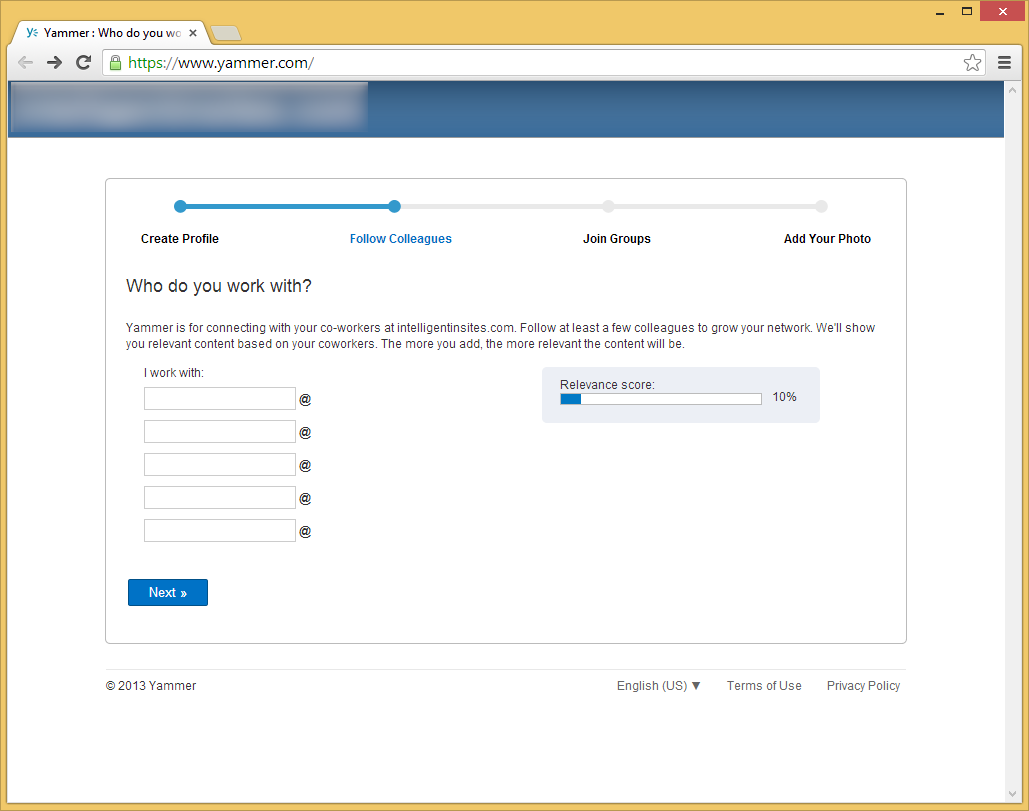
- Join or create any groups you would like and then click Next
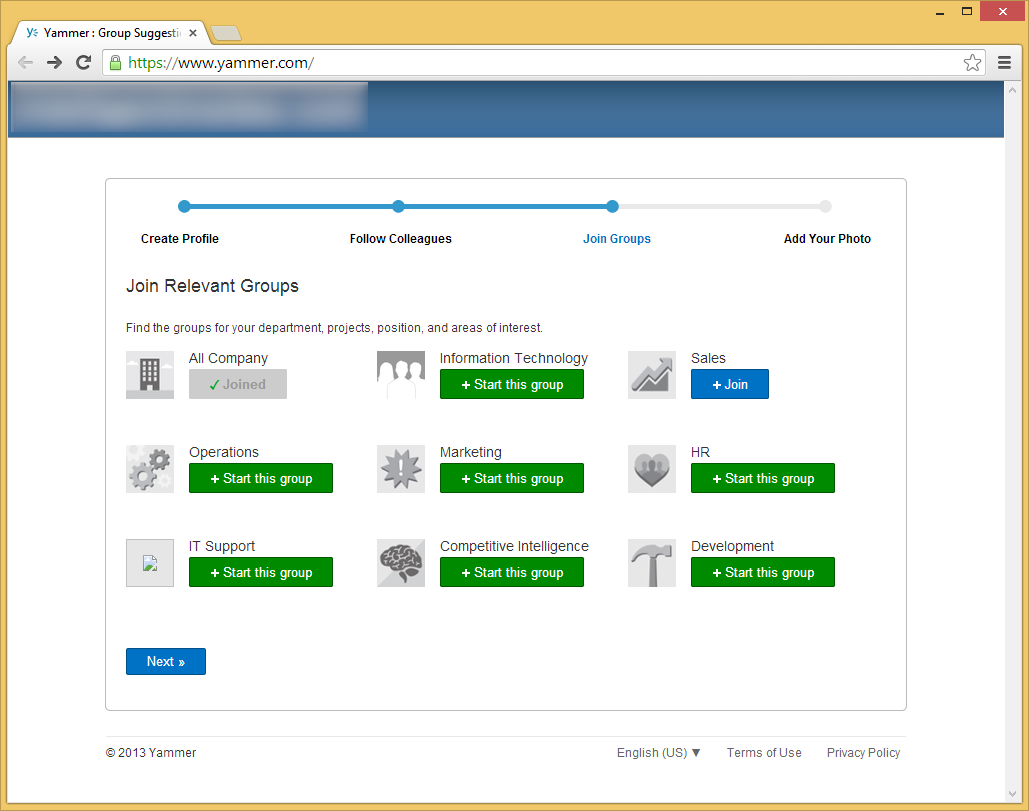
- Optionally, add a profile picture and click Save & Continue
- Click on the 3 dots in the top right corner and select Network Admin
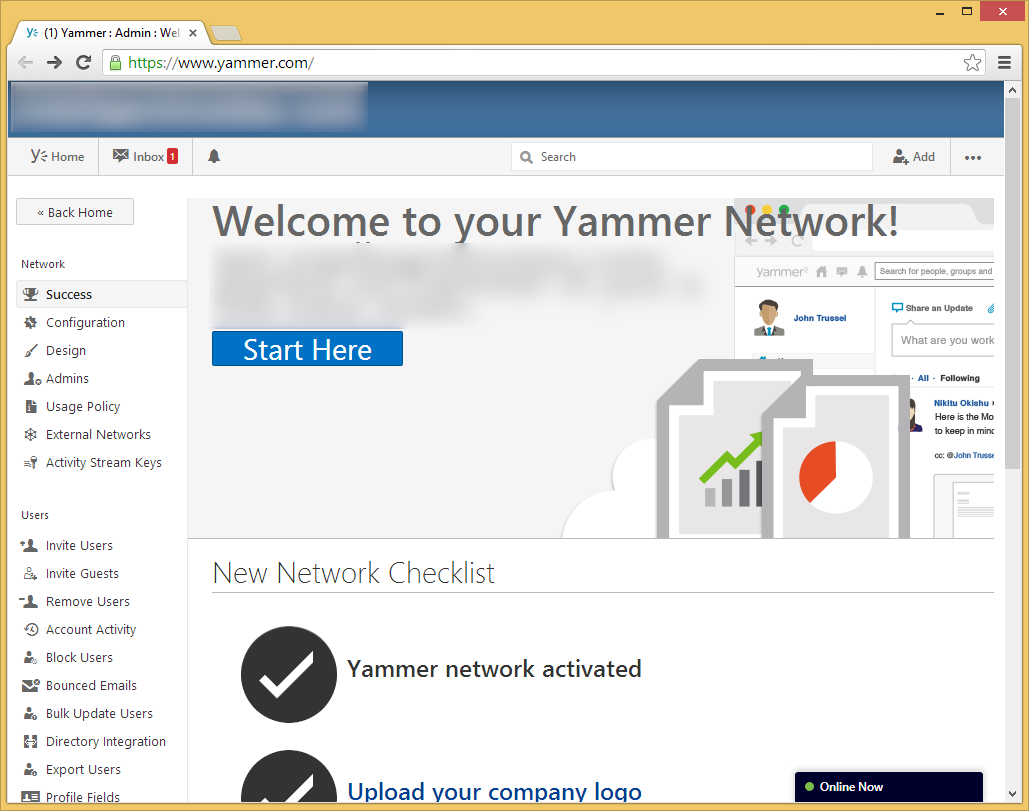
- Welcome to your Yammer Enterprise Admin portal! Here you can manage all aspects of Yammer for your organization.
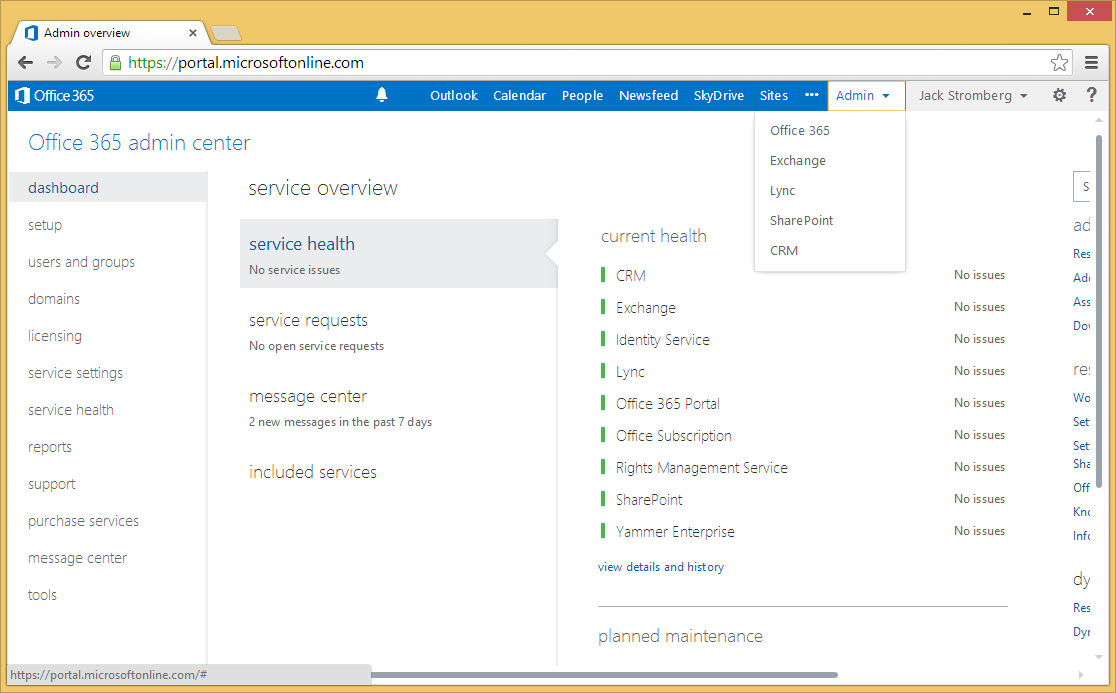
- Lastly, if you go back to your Office 365 Admin portal, you should see a link that will redirect you to the Yammer.com website.
FAQ
Does Yammer support single-sign on or ADFS?
Currently, Yammer does not support this integration at this time.
Will Yammer find users previously signed up with email addresses from @mydomain.com?
Yes
Does Microsoft have plans on continuing to integrate Yammer and Office 365?
Yes, Microsoft has announced they would like deeper integration with Office 365, more specifically with functionality in SharePoint. Quarter 4 of this year (2013) was their deadline for the first integration, and we have seen they have started to deliver. However, there are no specific dates yet of when users will be 100% synchronized between the two systems.
When I activate Yammer on Office 365 for my organization will it email all of my users to create profiles?
No, they will have to manually join or you will have to manually send them invites to create a separate Yammer account.