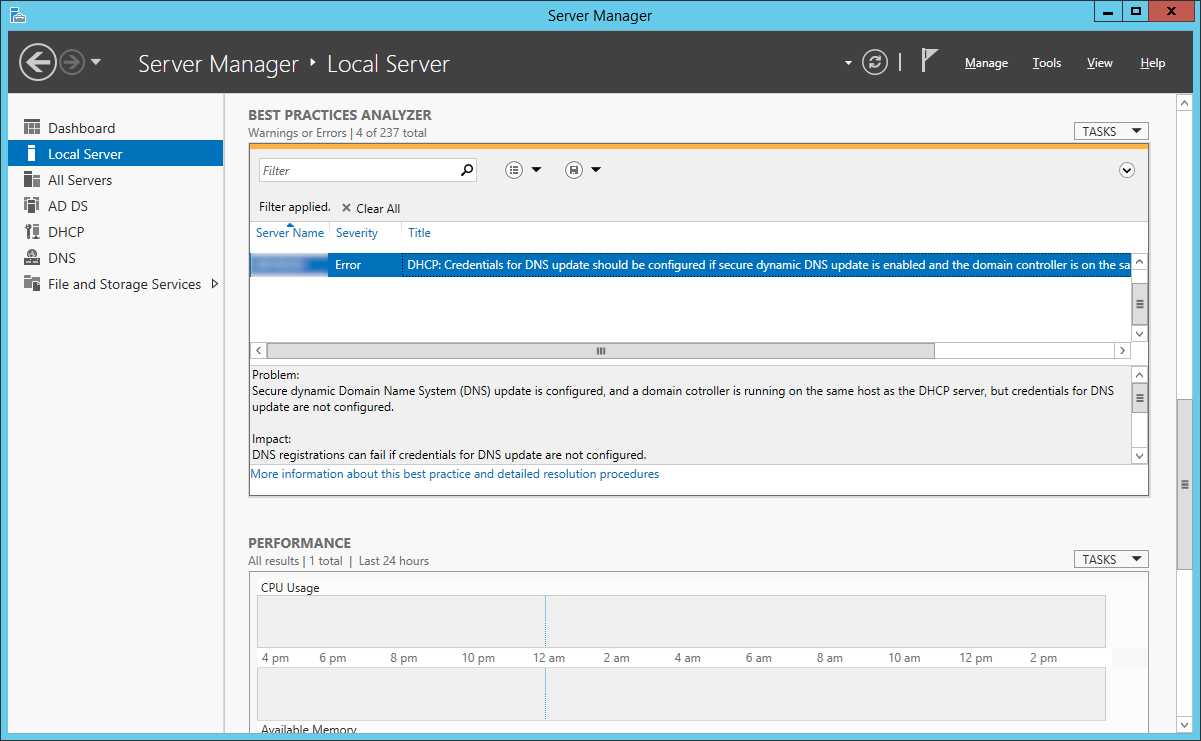
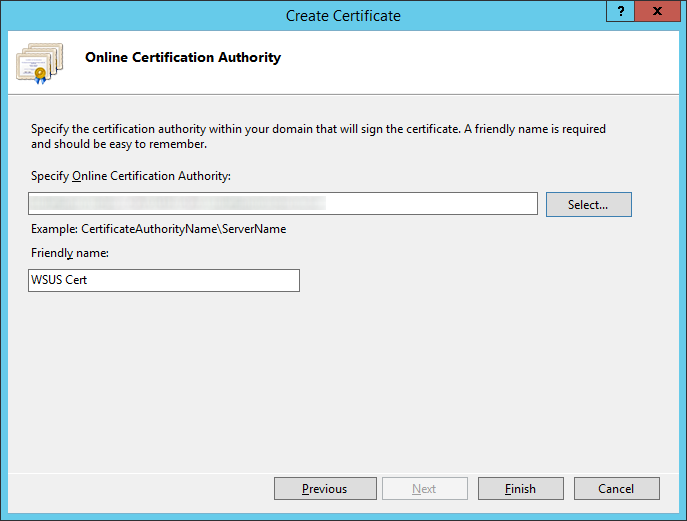
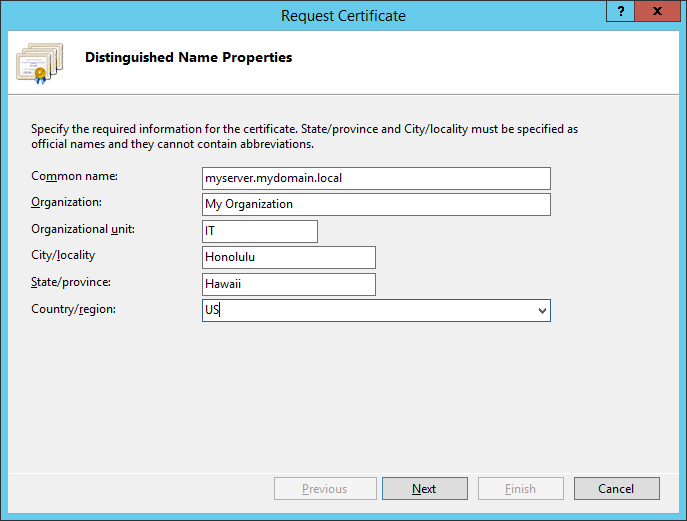
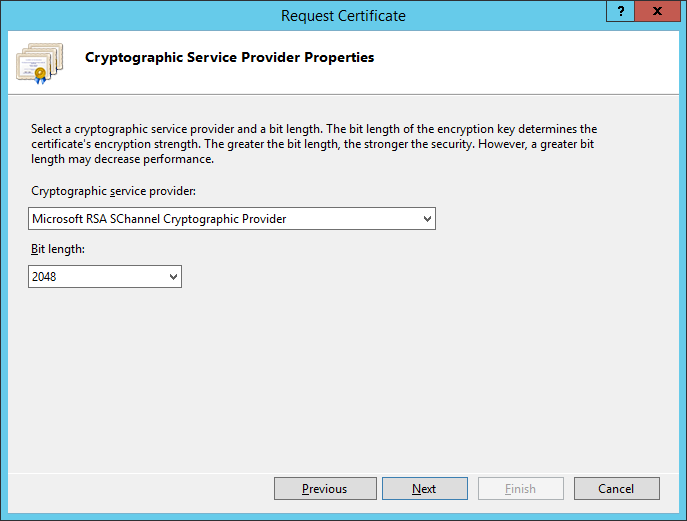
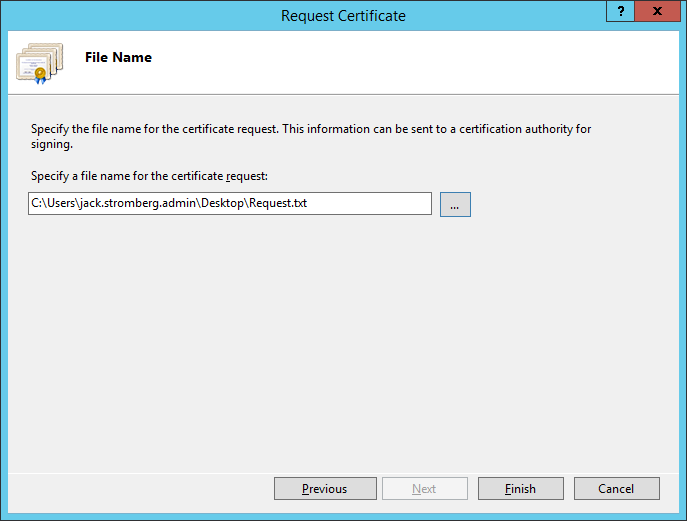
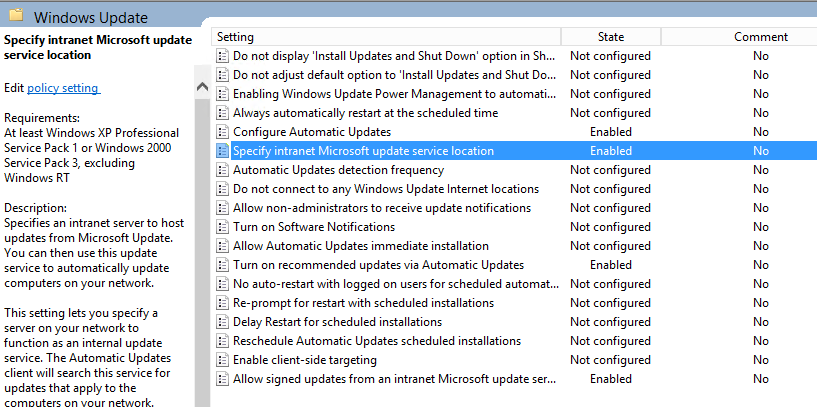
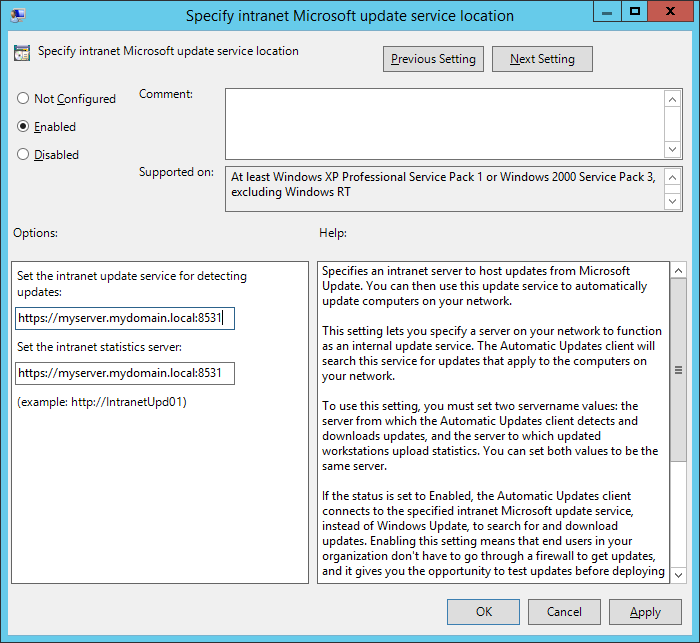
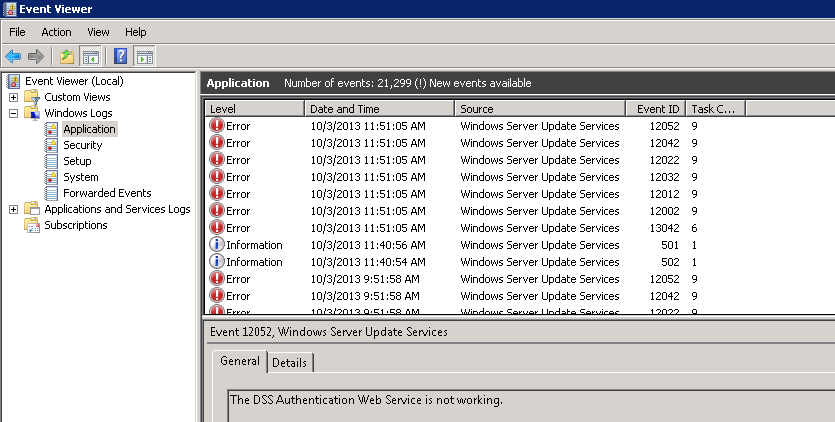
Copied from Microsoft, here is what we can achieve by configuring a KMS server on our local network for a windows domain: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff793434.aspx
KMS activates computers on a local network, eliminating the need for individual computers to connect to Microsoft. To do this, KMS uses a client–server topology. KMS client computers can locate KMS host computers by using Domain Name System (DNS) or a static configuration. KMS clients contact the KMS host by using remote procedure call (RPC). KMS can be hosted on computers that are running the Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, or Windows Server 2008 R2 operating systems.
- Go to the volume licensing center and grab a copy of the KMS key for your server OS
- Navigate to https://www.microsoft.com/Licensing/servicecenter/home.aspx
- Login
- Select Downloads and Keys
- Select Windows Server
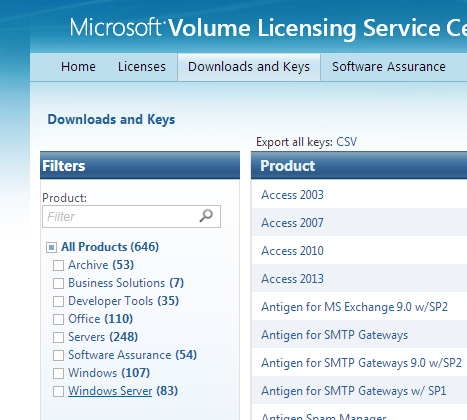
- Finder your server version and click Key
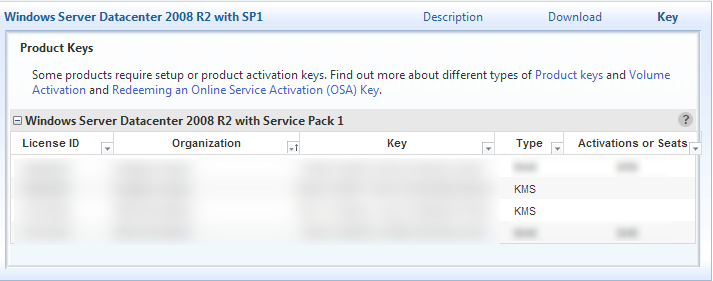
- Copy the KMS type key
- Login to the server you want to setup as the KMS server.
- Open up a command prompt as an administrator.
- Ensure you are in the system32 folder of Windows
- cd c:\Windows\System32
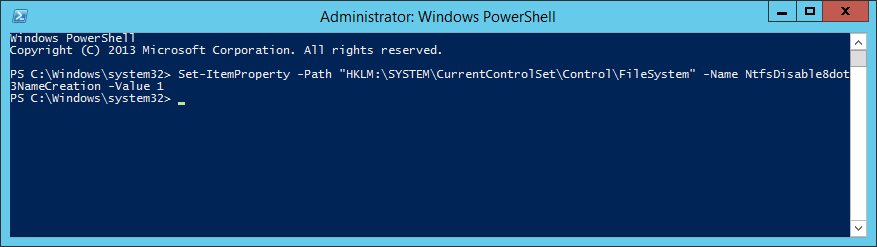
- Execute the following command to setup your license key
- cscript slmgr.vbs /ipk WINDOWS-KMS-LICENSE-KEY-HERE
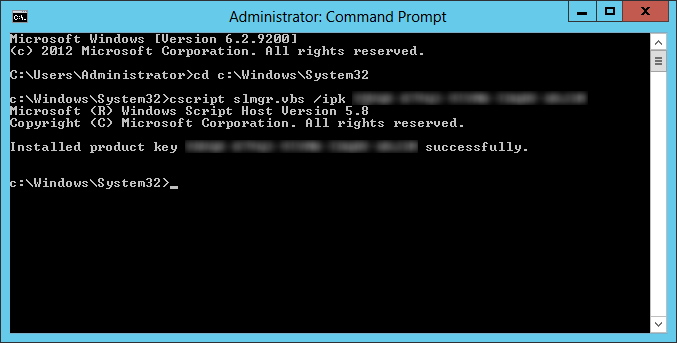
- Execute the following command to activate the host
- cscript slmgr.vbs /ato
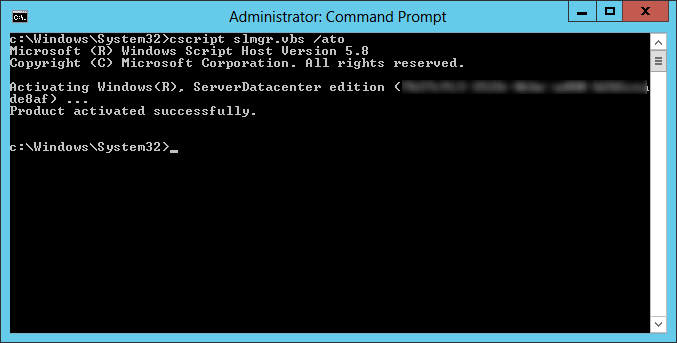
- Execute the following command to verify the host has the Key Management Service enabled
- cscript slmgr.vbs /dlv
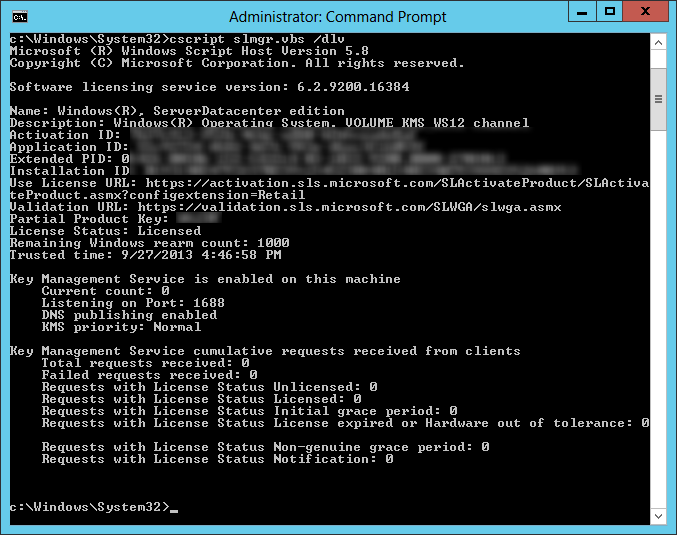
- Next, we need to open the firewall for the server to accept activation requests
- Open up Windows Firewall with Advanced Security

- Right click on Inbound Rules and select New Rule...
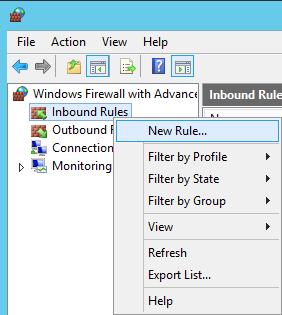
- Select Port and click Next >
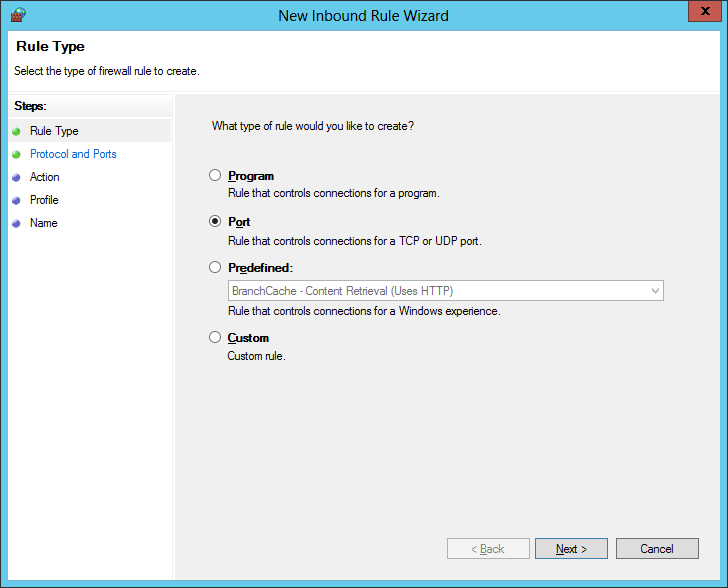
- Check TCP, check Specific Local Ports and enter port 1688, click Next >
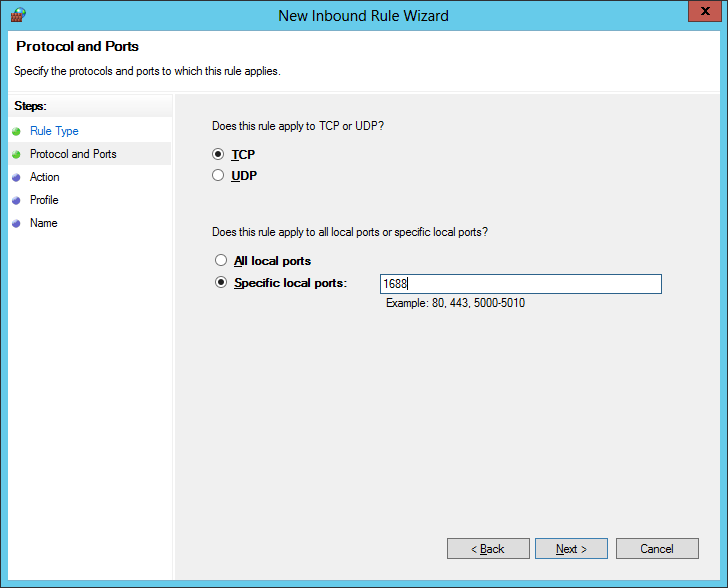
- Check Allow the connection and click Next >
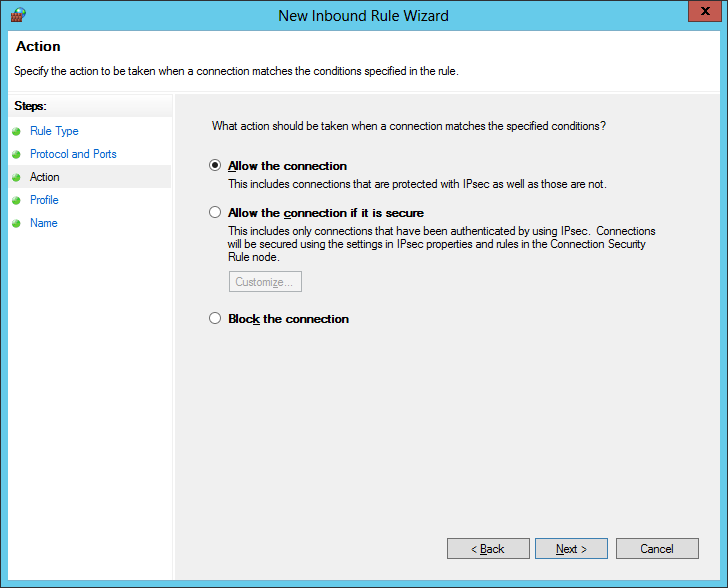
- Check Domain and click Next >
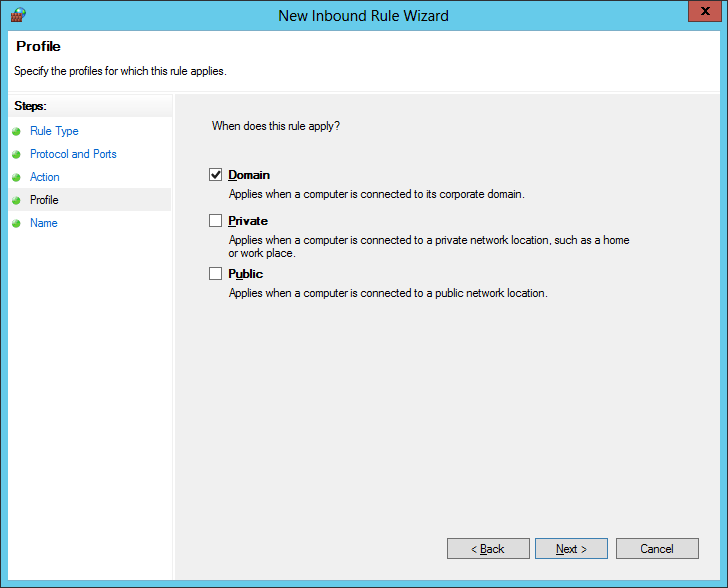
- Enter a name for the rule and click Finish
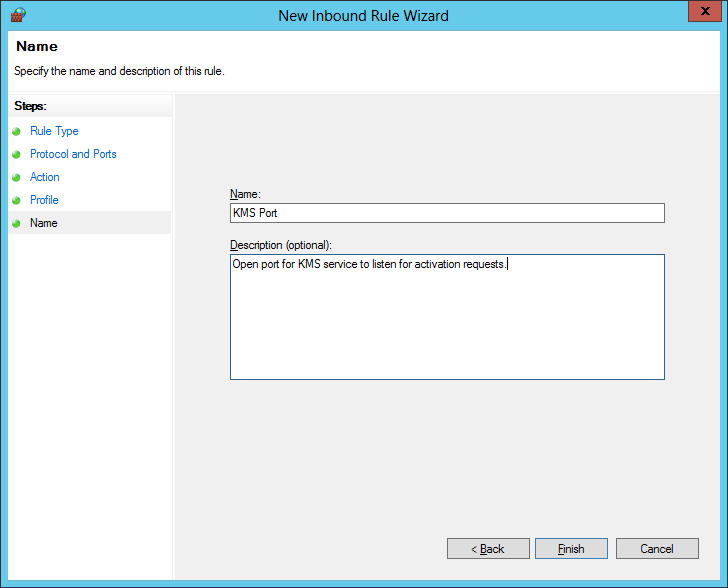
Congrats! Your KMS server should now be ready to accept activation requests!
Notes: Here is a full listing of the commands/switches you can execute using the Software Licensing Management Tool.
C:\Windows\System32>cscript slmgr.vbs
Microsoft (R) Windows Script Host Version 5.8
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Invalid combination of command parameters.
Windows Software Licensing Management Tool
Usage: slmgr.vbs [MachineName [User Password]] [<Option>]
MachineName: Name of remote machine (default is local machine)
User: Account with required privilege on remote machine
Password: password for the previous account
Global Options:
/ipk <Product Key>
Install product key (replaces existing key)
/ato [Activation ID]
Activate Windows
/dli [Activation ID | All]
Display license information (default: current license)
/dlv [Activation ID | All]
Display detailed license information (default: current license)
/xpr [Activation ID]
Expiration date for current license state
Advanced Options:
/cpky
Clear product key from the registry (prevents disclosure attacks)
/ilc <License file>
Install license
/rilc
Re-install system license files
/rearm
Reset the licensing status of the machine
/upk [Activation ID]
Uninstall product key
/dti [Activation ID]
Display Installation ID for offline activation
/atp <Confirmation ID> [Activation ID]
Activate product with user-provided Confirmation ID
Volume Licensing: Key Management Service (KMS) Client Options:
/skms <Name[:Port] | : port> [Activation ID]
Set the name and/or the port for the KMS computer this machine will use. IPv6 address must be specified in the format [hostname]:port
/ckms [Activation ID]
Clear name of KMS computer used (sets the port to the default)
/skms-domain <FQDN> [Activation ID]
Set the specific DNS domain in which all KMS SRV records can be found. This setting has no effect if the specific single KMS host is set via /skms option.
/ckms-domain [Activation ID]
Clear the specific DNS domain in which all KMS SRV records can be found. The specific KMS host will be used if set via /skms. Otherwise default KMS auto-discovery will be used.
/skhc
Enable KMS host caching
/ckhc
Disable KMS host caching
Volume Licensing: Token-based Activation Options:
/lil
List installed Token-based Activation Issuance Licenses
/ril <ILID> <ILvID>
Remove installed Token-based Activation Issuance License
/ltc
List Token-based Activation Certificates
/fta <Certificate Thumbprint> [<PIN>]
Force Token-based Activation
Volume Licensing: Key Management Service (KMS) Options:
/sprt <Port>
Set TCP port KMS will use to communicate with clients
/sai <Activation Interval>
Set interval (minutes) for unactivated clients to attempt KMS connection. The activation interval must be between 15 minutes (min) and 30 days (max) although the default (2 hours) is recommended.
/sri <Renewal Interval>
Set renewal interval (minutes) for activated clients to attempt KMS connection. The renewal interval must be between 15 minutes (min) and 30 days (max) although the default (7 days) is recommended.
/sdns
Enable DNS publishing by KMS (default)
/cdns
Disable DNS publishing by KMS
/spri
Set KMS priority to normal (default)
/cpri
Set KMS priority to low
/act-type [Activation-Type] [Activation ID]
Set activation type to 1 (for AD) or 2 (for KMS) or 3 (for Token) or 0 (for all).
Volume Licensing: Active Directory (AD) Activation Options:
/ad-activation-online <Product Key> [Activation Object name]
Activate AD (Active Directory) forest with user-provided product key
/ad-activation-get-iid <Product Key>
Display Installation ID for AD (Active Directory) forest
/ad-activation-apply-cid <Product Key> <Confirmation ID> [Activation Object name]
Activate AD (Active Directory) forest with user-provided product key and Confirmation ID
/ao-list
Display Activation Objects in AD (Active Directory)
/del-ao <Activation Object DN | Activation Object RDN>
Delete Activation Objects in AD (Active Directory) for user-provided Activation Object