Here are the steps to configure SSL on your servers running the Windows Server Update Services. This guide was written using Server 2012 R2, however it should be the same steps for Windows Server 2008 R2 as well. This guide also assumes you have a working instance of WSUS installed and configured, using default ports.
- Login to your WSUS server
- Open up Server Manager
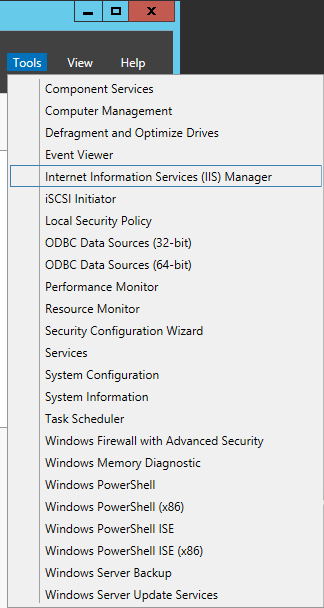
- Select Tools -> Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager
- Generate a SSL certificate
- Click on your Server and select Server Certificates
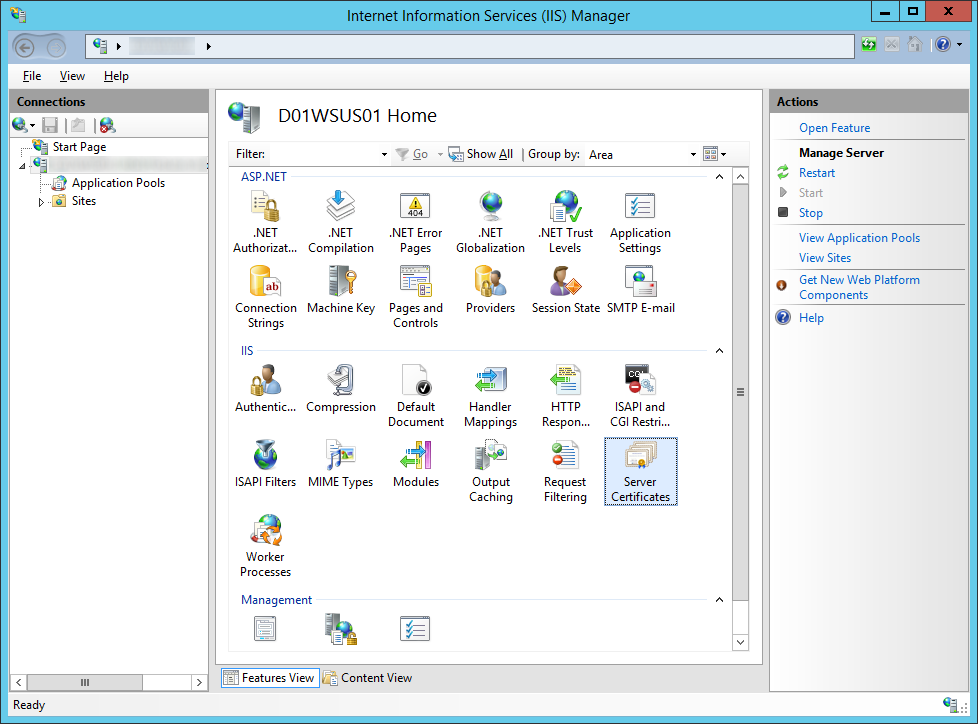
- If you have your own PKI environment, follow these steps, if not, jump to step three
- If you need to submit a certificate request to an external certificate authority like Goaddy, Verisgn, Comodo; follow these steps
- Click Create Certificate Request on the right side
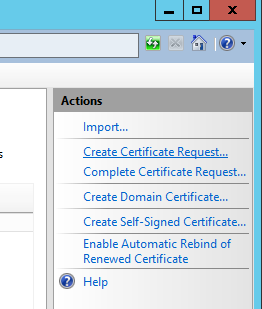
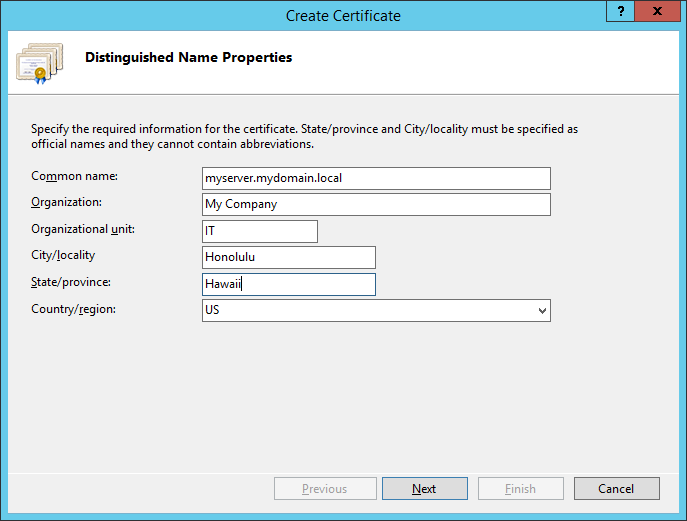
- Fill out the Distinguished Name Properties and click Next
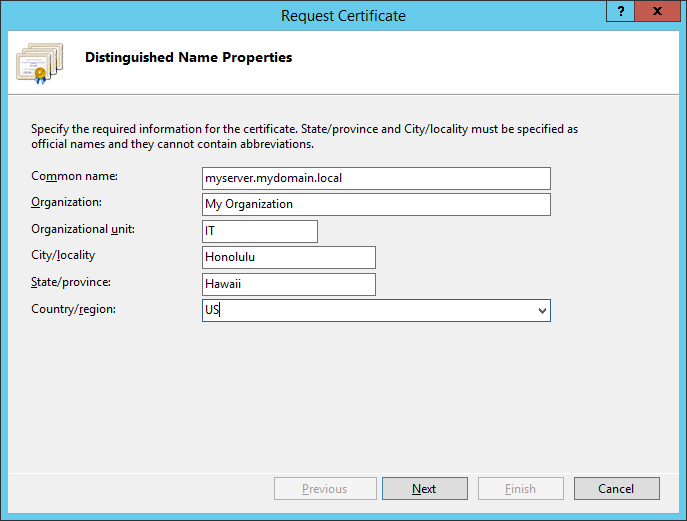
- Change the Bit length to 2048 and click Next
- Select a location on where to place the CSR file that will be generated by the wizard and click Finish
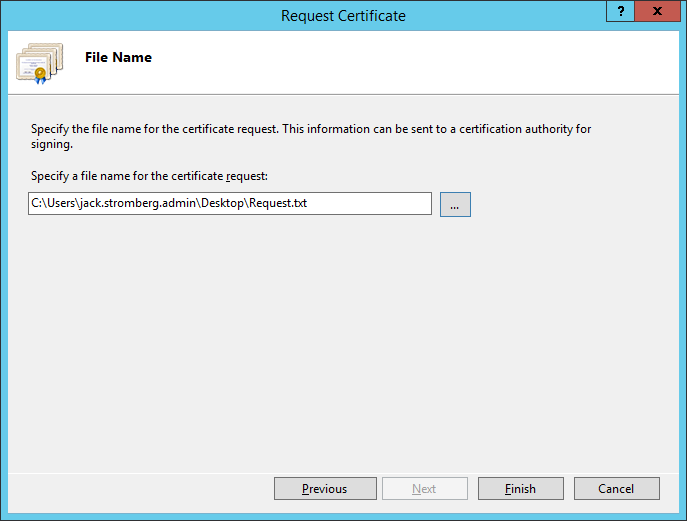
- At this point, send the request to your certificate authority (like GoDaddy, Verisign, or your own internal certificate authority). You should receive back a .cer file once the claim has been fulfilled.
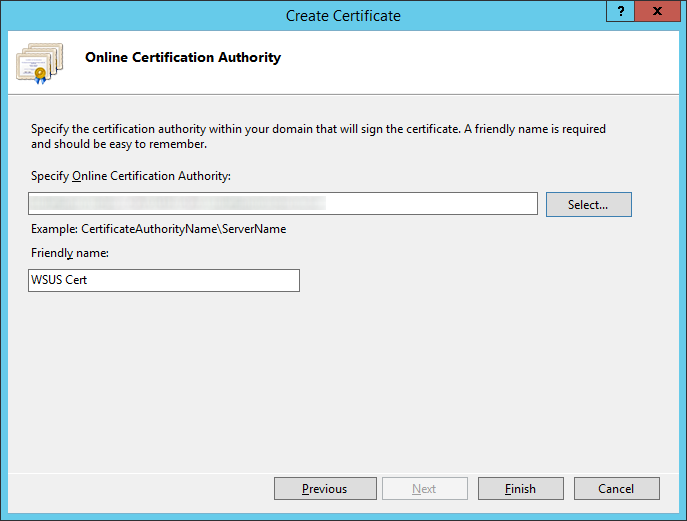
- Click on Complete Certificate Request on the right side
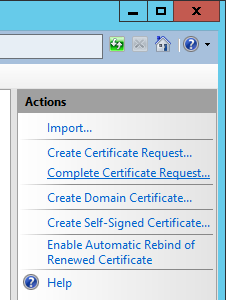
- Select the .cer file that your public certificate authority provided you, type in a friendly name (this can be anything), select Web Hosting for the certificate store, and click OK
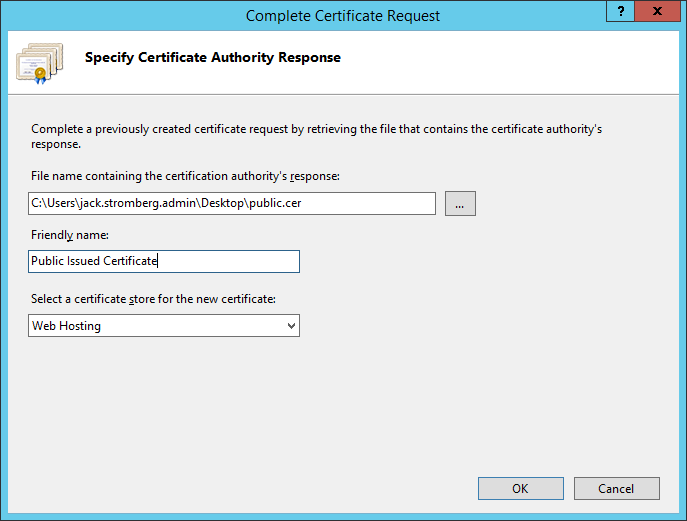
- Click Create Certificate Request on the right side
- Click on your Server and select Server Certificates
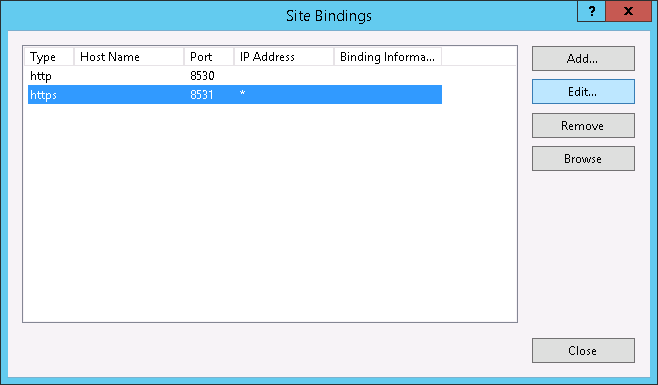
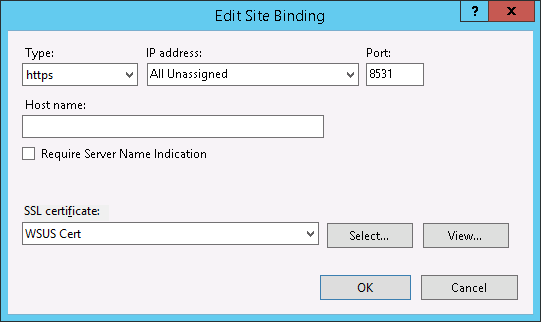
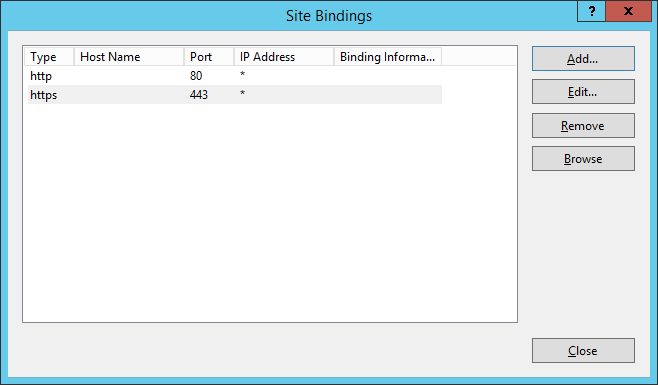
- Next, we need to bind the SSL certificate to your network adapter.
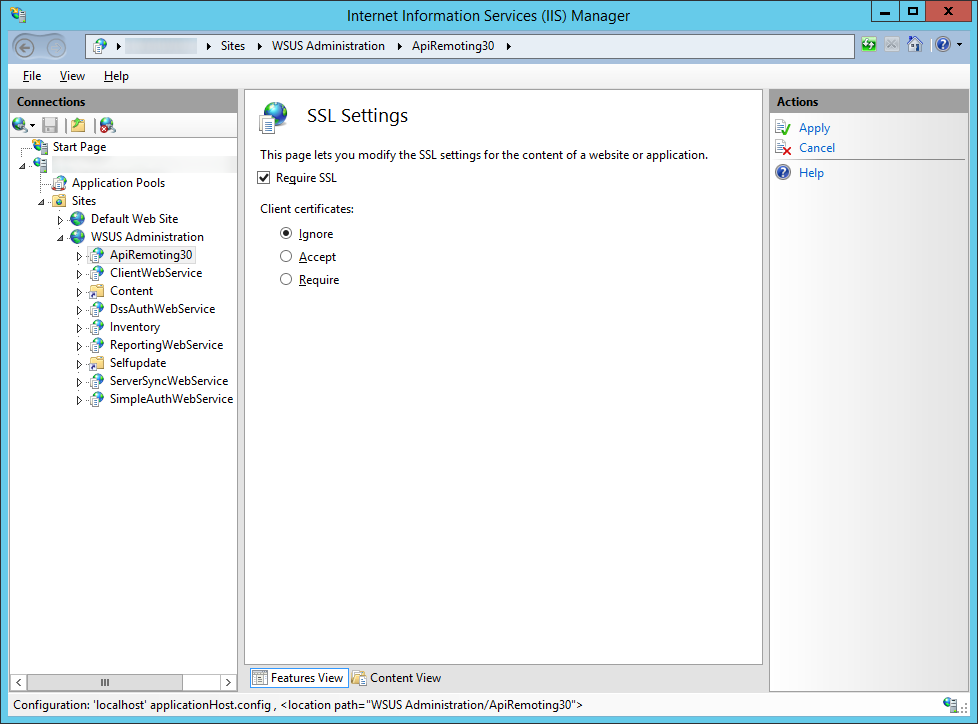
- Next, we need to enforce SSL encryption on the following virtual roots
• ApiRemoting30
• ClientWebService
• DSSAuthWebService
• ServerSyncWebService
• SimpleAuthWebService - Next, we need to execute a command to tell WSUS to use ssl
- Restart the WSUS server to make sure all changes take effect. You should be able to bring up the WSUS management console if all went well.
- Configure your clients to connect via SSL to the WSUS server via Group Policy
- Login to your domain controller
- Open up Server Manager

- Open up Group Policy Management
- Right click on the policy you want to edit and select Edit
- Expand Computer Configuration -> Polices -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Update
- Double click on Specify intranet Microsoft update service location
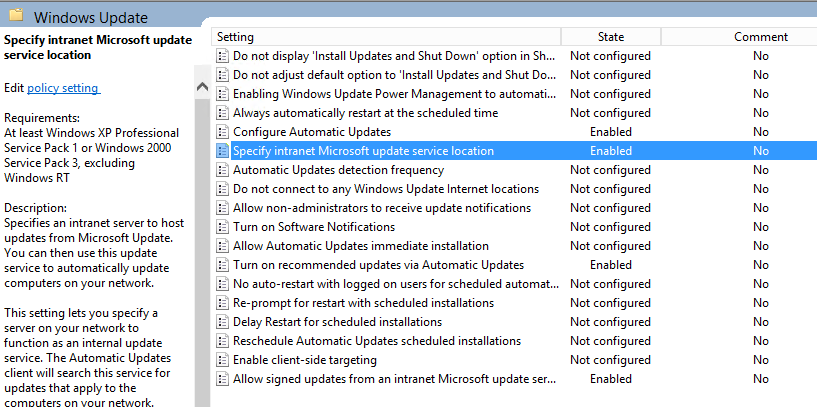
- Change the intranet update service url to https and specify port 8531 and then click Apply.
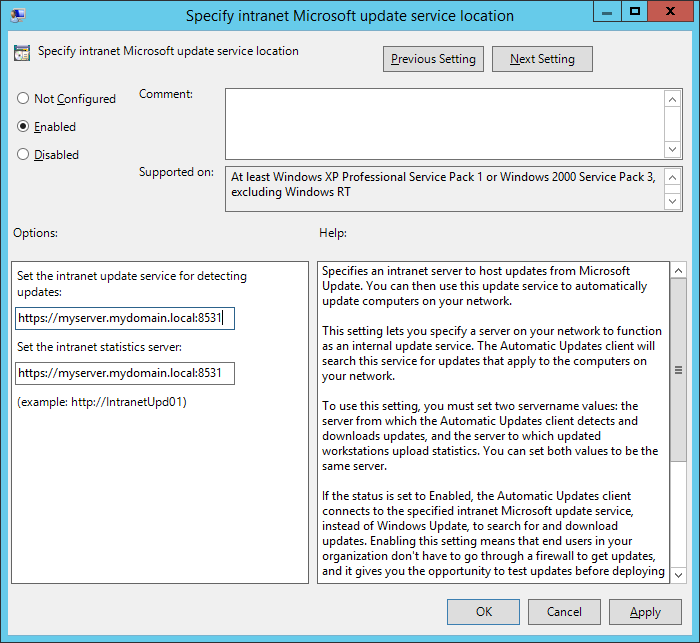
That should do it! Try doing a gpupdate /force on your local machine and the check for windows updates. If windows successfully completes checking for updates, you should be good to go! 🙂
Notes: Official documentation from Microsoft in regards to using SSL and WSUS can be found here: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh852346.aspx#consswsus