With Azure PowerShell modules changing all the time and the recent introduction of the PowerShell modules being renamed from AzureRm to Az, you may want to totally uninstall all modules and reinstall to make sure you are using the latest and greatest modules.
To do so, StackOverflow user BlueSky, wrote a handy dandy script that will go through and cleanup all the Azure(RM)(AD) modules. Simply open up PowerShell as an Administrator and execute the following PowerShell workflow/commands:
workflow Uninstall-AzureModules
{
$Modules = @()
$Modules += (Get-Module -ListAvailable Azure*).Name
$Modules += (Get-Module -ListAvailable Az.*).Name
Foreach -parallel ($Module in ($Modules | Get-Unique))
{
Write-Output ("Uninstalling: $Module")
Uninstall-Module $Module -Force
}
}
Uninstall-AzureModules
Uninstall-AzureModules #second invocation to truly remove everything
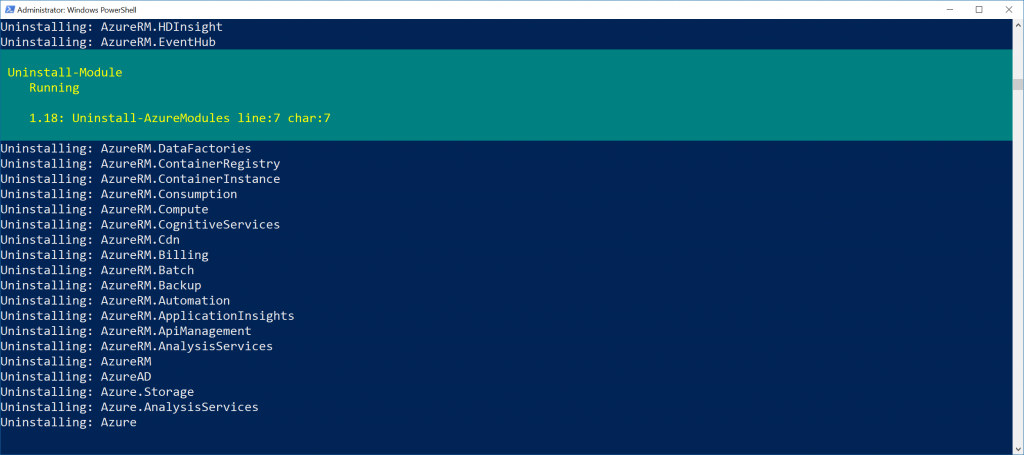
The thing about the PowerShell script above being a workflow is this allows you to remove all the modules in parallel vs one-by-one. Here's a screenshot of the script in action.
Hope this helps!